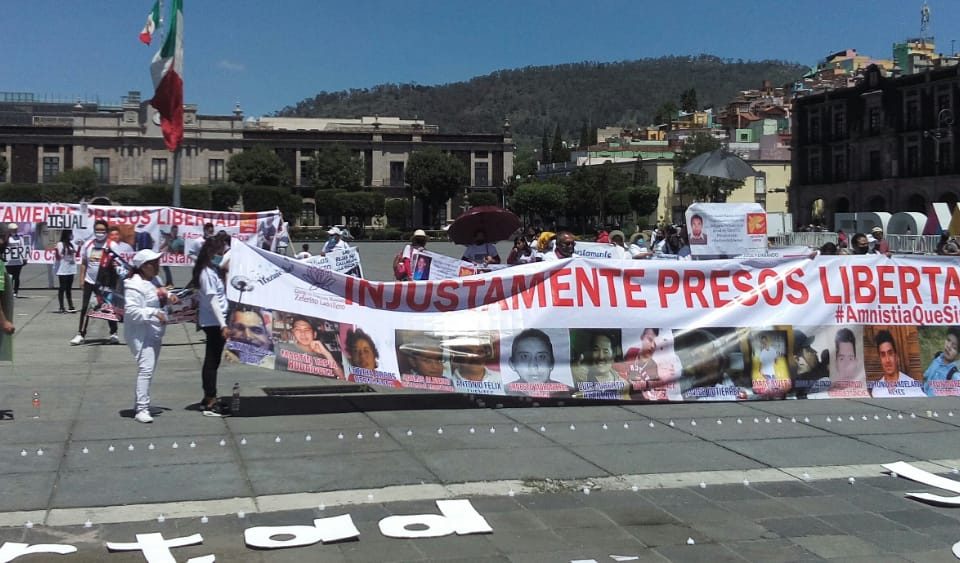
Ballot selling costs in 2018
August 2, 2018
Odín Dupeyron returns to Toluca
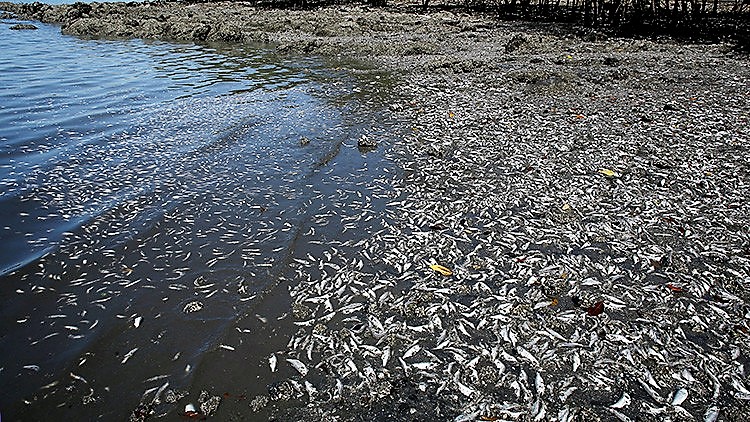
August 5, 2018An Oceanic Dead Zone was reported in the northeast of the Gulf of Mexico

HIGHLIGHTS
An Oceanic Dead Zone was reported in the northeast of the Gulf of Mexico

Researchers from U.S.A and from international organizations, United Nations among them, have detected a type of sea contamination that can be reversed but causes death to marine flora and fauna at the time that kills off submarine oxygen which is essential for life.
In the north of the Gulf of Mexico, in American territory at the height of the Mississippi River mouth in the Atlantic, satellite photographs have detected a black spot- scientifically known as Dead Zone- which is an area that kills every living being (marine flora and fauna) that remains inside the spot.
Within a radius of more than 22 thousand square kilometers, which is the biggest size of the ‘Dead Zones´, plant and animal kingdom living beings are condemned to disappear. This has always been the case.
Among the species are included all sort of bivalve mollusks (with shell), sponges, tunicates and several other organisms, that usually inhabit at the bottom of the sea, which will hopelessly die as a consequence of the lack of oxygen.
This has been the case in the last 25 years in the North Atlantic zone in the Gulf of Mexico, as a result of the intensive application of fertilizer and agrochemicals in at least nine states of the American Union.
Agriculture in an effort to achieve a higher productivity of the lands, mainly sown under corn, apply fertilizers and pesticides in an indiscriminate manner causing to fill the Mississippi stream with toxic waste.
The term ´Dead Zone’ is applied owing to the lack of oxygen which stops the development of life. This phenomenon is caused by the application of nitrogenized fertilizers to the crops which wastes are carried out eventually by the rain to the riverbed during the rainy season and hurricanes until the arrival to the sea.
Fertilizers based on nitrogen, phosphorus and other elements conducive the excessive development of seaweed and several other aquatic plants that accomplish the life cycle, but its decomposition requires gigantic amounts of oxygen that are taken out of the sea water and this threatens every other vegetal life within the zone.
Oceanic ‘Dead Zones’ are estimated to keep a constant growing on the basis of the amplification of human activities and the amount of physical and chemical waste in the superficial and subaquatic water bodies. These 400 ‘spots’ in the ocean have reached a surface superior to 250 thousand square kilometers.
Results from the Evaluación del Ecosistema del Milenio (Millennial Ecosystem Evaluation) carried out by the initiative of the United Nations, instruct countries and their governments in order to take preventive and operative measures to allow a decrease and disappear a load of waste from fertilizers and agrochemicals in the water bodies that reach the sea.
This phenomenon occurred ten decades ago for the same reason (dumping toxic waste) in the border of the Black Sea with Russia. Contaminants ceased to be applied and the Dead Zone was recovered. In this manner, it was possible to restore the marine flora and fauna to the place in order to reactive fishing activities and economic dynamics surrounding a healthy water body.
Nowadays, some countries are still fighting against ‘Dead Zones´ situations like in the eastern sea of China, the Black Sea in Russia, in the Kattegat Strait, in the Bay of Chesapeake, in U.S.A and in the northeast region of the Gulf of Mexico.
Pascacio Taboada
Translator: Fabian Peñaloza
In the north of the Gulf of Mexico, in American territory at the height of the Mississippi River mouth in the Atlantic, satellite photographs have detected a black spot- scientifically known as Dead Zone- which is an area that kills every living being (marine flora and fauna) that remains inside the spot.
Within a radius of more than 22 thousand square kilometers, which is the biggest size of the ‘Dead Zones´, plant and animal kingdom living beings are condemned to disappear. This has always been the case.
Among the species are included all sort of bivalve mollusks (with shell), sponges, tunicates and several other organisms, that usually inhabit at the bottom of the sea, which will hopelessly die as a consequence of the lack of oxygen.
This has been the case in the last 25 years in the North Atlantic zone in the Gulf of Mexico, as a result of the intensive application of fertilizer and agrochemicals in at least nine states of the American Union.
Agriculture in an effort to achieve a higher productivity of the lands, mainly sown under corn, apply fertilizers and pesticides in an indiscriminate manner causing to fill the Mississippi stream with toxic waste.
The term ´Dead Zone’ is applied owing to the lack of oxygen which stops the development of life. This phenomenon is caused by the application of nitrogenized fertilizers to the crops which wastes are carried out eventually by the rain to the riverbed during the rainy season and hurricanes until the arrival to the sea.
Fertilizers based on nitrogen, phosphorus and other elements conducive the excessive development of seaweed and several other aquatic plants that accomplish the life cycle, but its decomposition requires gigantic amounts of oxygen that are taken out of the sea water and this threatens every other vegetal life within the zone.
Oceanic ‘Dead Zones’ are estimated to keep a constant growing on the basis of the amplification of human activities and the amount of physical and chemical waste in the superficial and subaquatic water bodies. These 400 ‘spots’ in the ocean have reached a surface superior to 250 thousand square kilometers.
Results from the Evaluación del Ecosistema del Milenio (Millennial Ecosystem Evaluation) carried out by the initiative of the United Nations, instruct countries and their governments in order to take preventive and operative measures to allow a decrease and disappear a load of waste from fertilizers and agrochemicals in the water bodies that reach the sea.
This phenomenon occurred ten decades ago for the same reason (dumping toxic waste) in the border of the Black Sea with Russia. Contaminants ceased to be applied and the Dead Zone was recovered. In this manner, it was possible to restore the marine flora and fauna to the place in order to reactive fishing activities and economic dynamics surrounding a healthy water body.
Nowadays, some countries are still fighting against ‘Dead Zones´ situations like in the eastern sea of China, the Black Sea in Russia, in the Kattegat Strait, in the Bay of Chesapeake, in U.S.A and in the northeast region of the Gulf of Mexico.
Pascacio Taboada
Translator: Fabian Peñaloza